Introduction
Prior to reading this article, I would recommend first reading my blog: Optimistic Concurrency in Databases.
The ETag (or entity tag) HTTP response header is an identifier for a specific version of a resource.
In this article, we will discuss how this header is useful to prevent simultaneous updates of a resource from overwriting each other.
Problem
Let's first illustrate the problem by considering a REST API that does not leverage ETag headers.
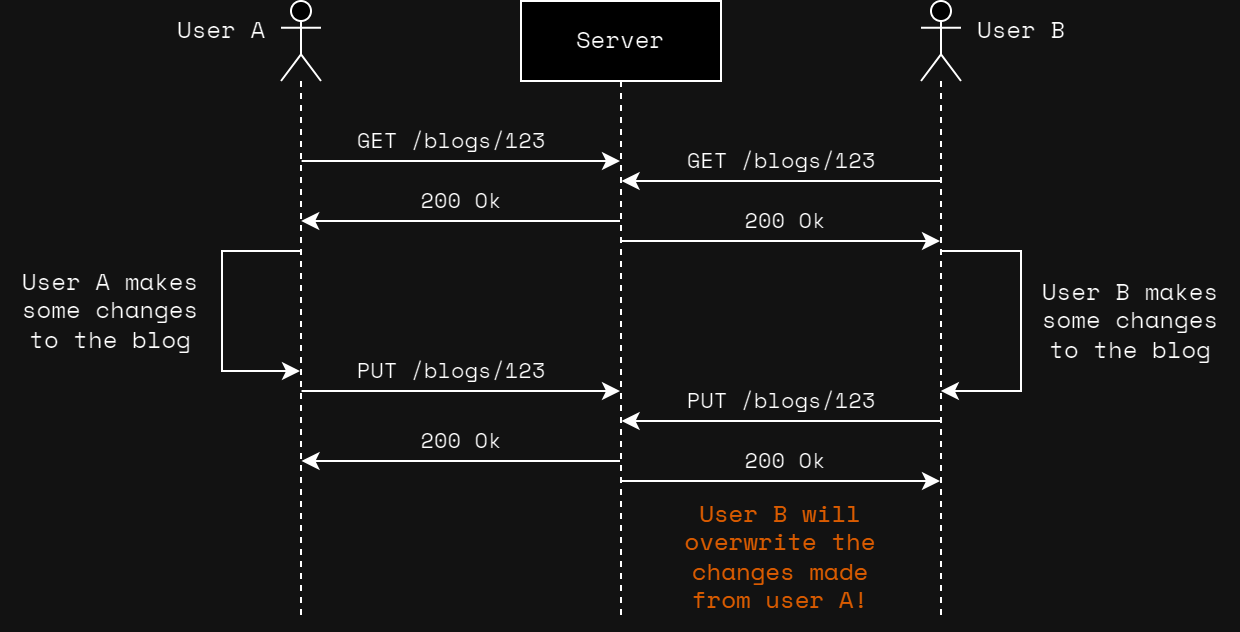
Consider a blog website, where multiple users can make edits to the same blog post. Here is a simplified representation of the REST API:
GET /blogs/{blogId}
PUT /blogs/{blogId}GET /blogs/{blogId}
PUT /blogs/{blogId}Now imagine that two users (User A and User B) both make edits at the same time:
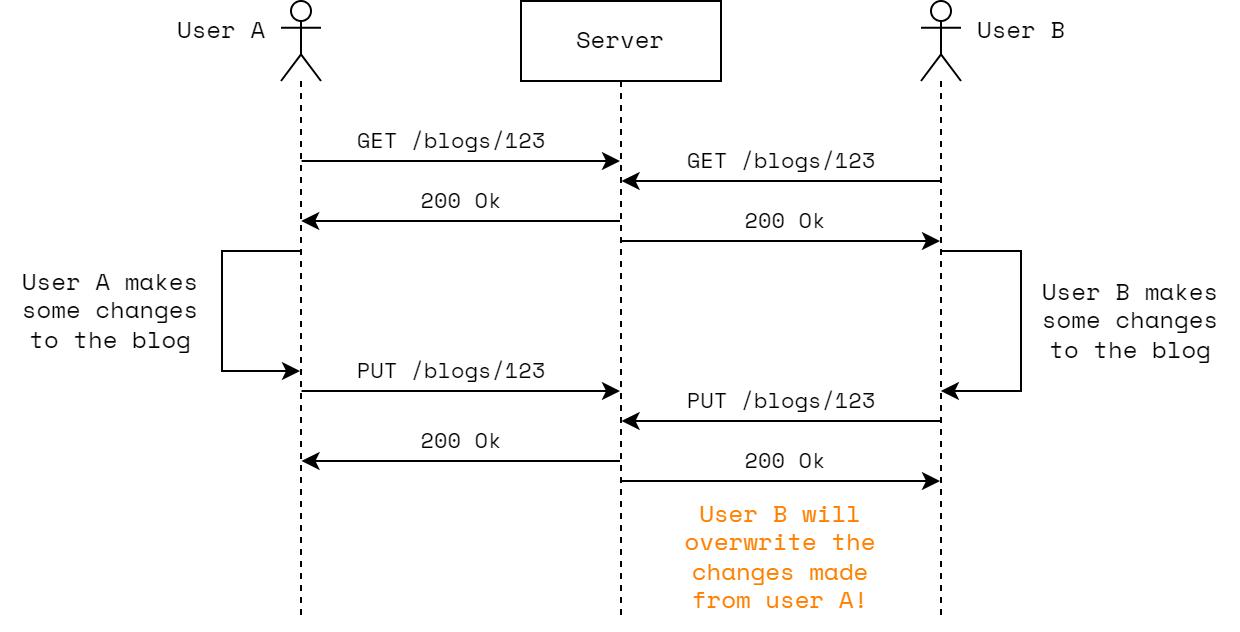
As illustrated in the diagram above, without ETag it is possible to overwrite changes made by another user!
Solution
This problem can be resolved by leveraging ETag and If-Match headers.
What is the ETag Header?
An ETag is a version identifier for a resource, ensuring updates are made only when the current version is matched.
This is returned as a header in the GET endpoint of a resource.
What is the If-Match Header?
The If-Match header is used in HTTP requests to ensure that a resource is updated only if it matches a specific version.
In more detail, it contains the ETag which can be retrieved by the GET endpoint of a resource.
ETag formats (Weak, Strong)
Weak
Weak ETag values of two representations of the same resources might be semantically equivalent, but not byte-for-byte identical.
ETag: W/"0815"ETag: W/"0815"Strong
Strong ETag values uniquely represent the requested resource. It is a string of ASCII characters placed between double quotes, like "675af34563dc-tr34".
The ETag can be generated as a hash of the content, a hash of the last modification timestamp, or just a version number.
ETag: "33a64df551425fcc55e4d42a148795d9f25f89d4"ETag: "33a64df551425fcc55e4d42a148795d9f25f89d4"ETag in Concurrency Control
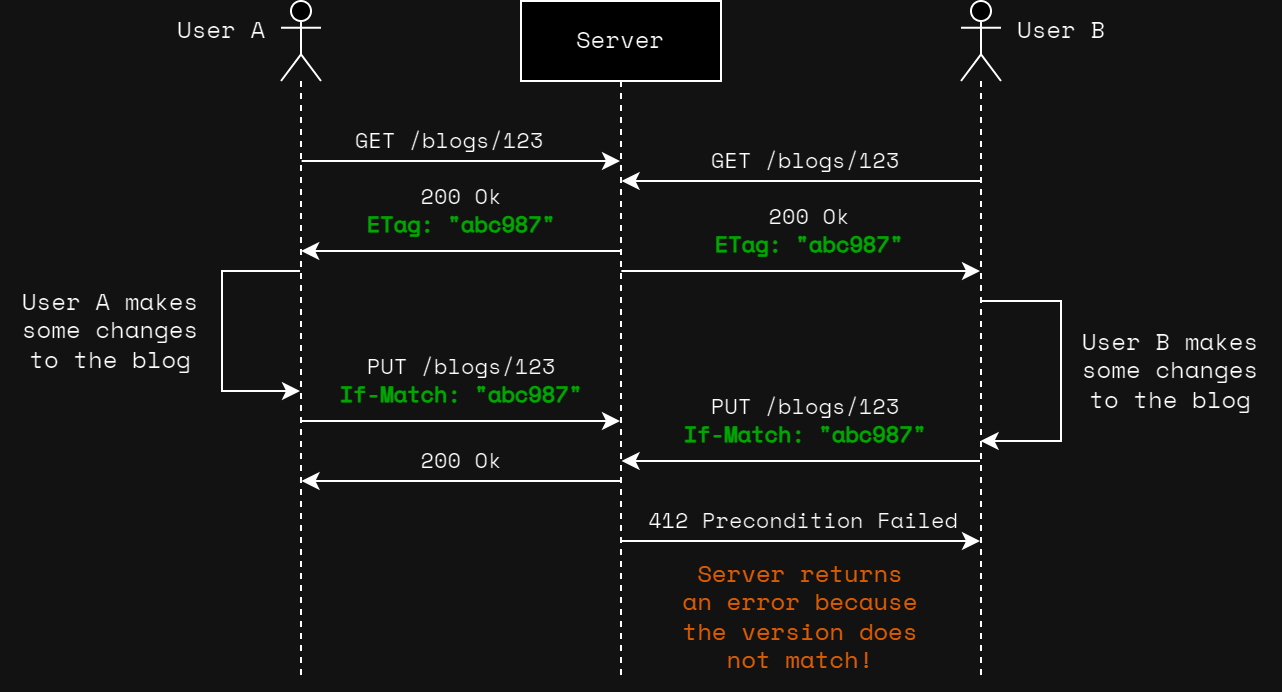
The image below illustrates a modified example where ETag and If-Match headers are used to prevent simultaneous updates from overwriting each other.
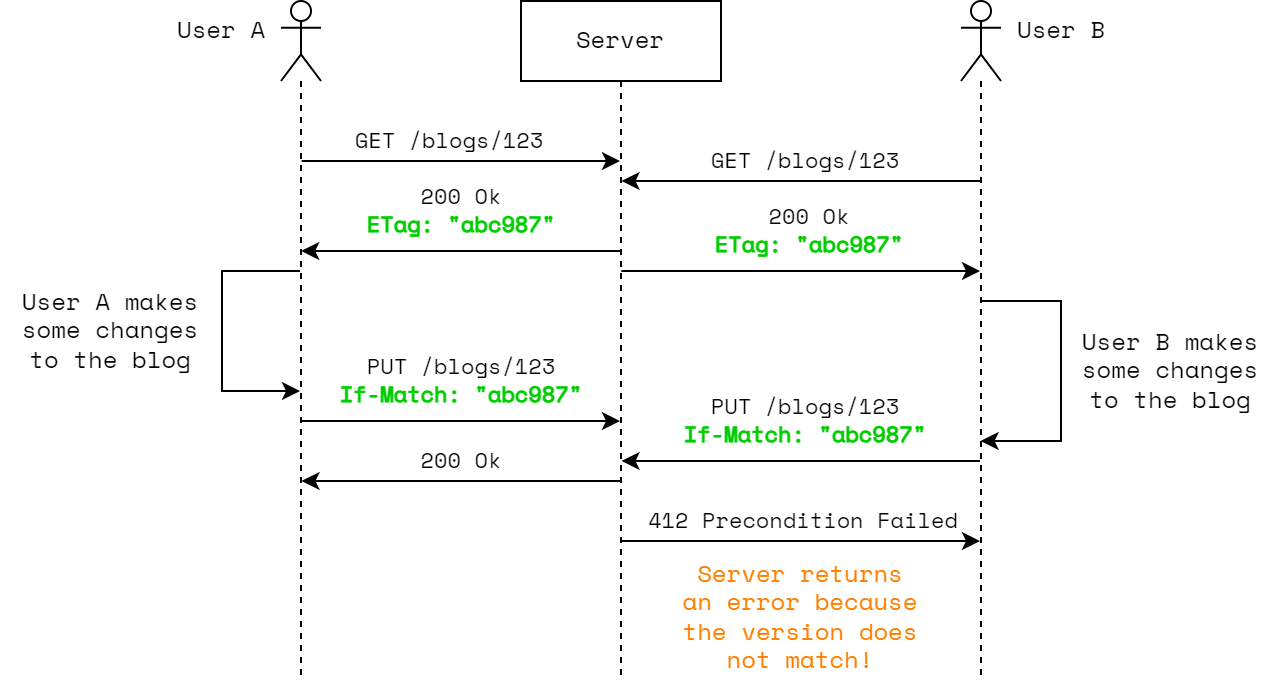
When performing the update via the PUT /blogs/{blogId}, an If-Match header is passed (with the ETag value).
If the version of the resource does not match, a 412 (Precondition Failed) response will be returned.
As a result, User B will not overwrite the changes made by User A!
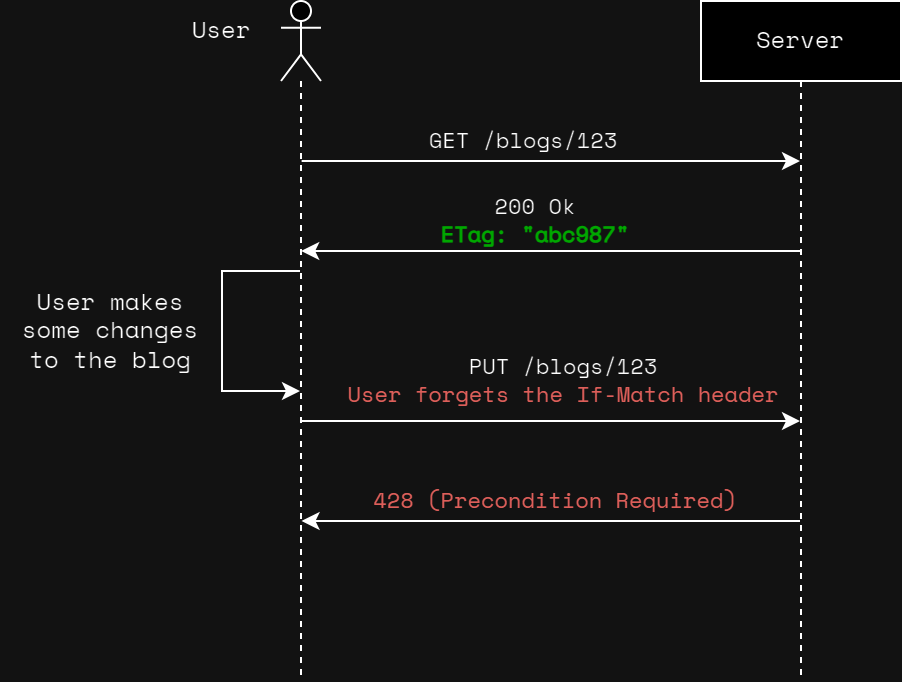
What Happens Without If-Match Header
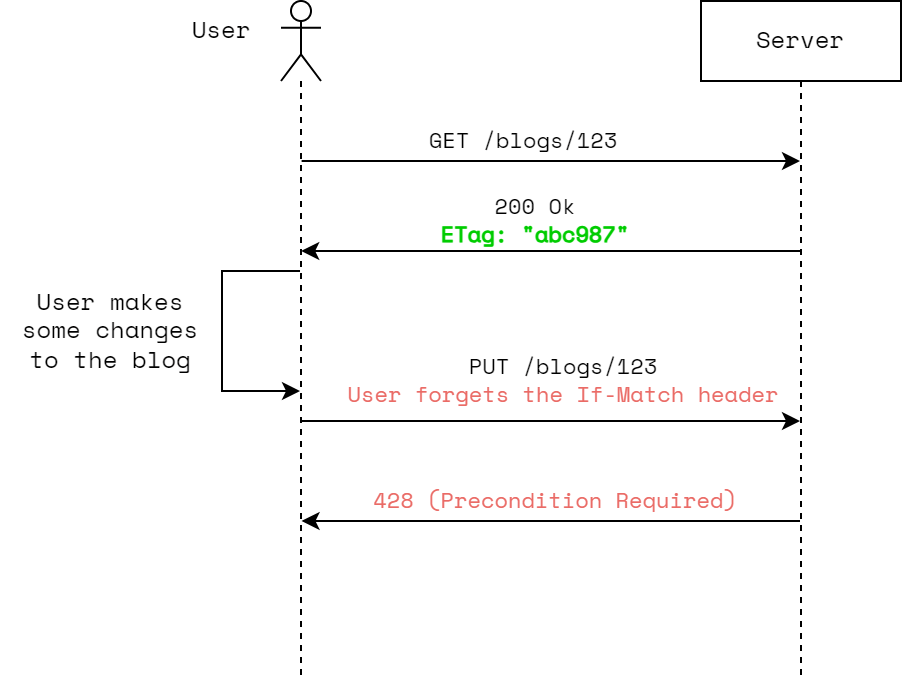
In the case that no If-Match header is provided to the PUT /blogs/{blogId}, the server can respond with 428 (Precondition Required) response.
Conclusion
- The
ETag(or entity tag) HTTP response header is an identifier for a specific version of a resource. - It is useful to prevent simultaneous updates of a resource from overwriting each other by returning a
412 (Precondition Failed)response when theIf-Matchheader does not match the expected value.